Setting Up The Salesforce Lambdas Manually
Below are manual setup instructions for the Salesforce Lambdas.
Prerequisite Configuration and Data Collection
In order to successfully deploy and utilize the functions in the Amazon Connect Salesforce Lambda package, you will need to validate and configure some items in your Salesforce Org and gather some information from your Amazon Connect instance.
Check your Salesforce API version
Create a new Connected App
Create a new API user
Gather Amazon Connect information
As you are preparing to deploy the package, it is a good idea to open a text editor and note information as you configure the environment. We will point out the items you will need to provide.
Check your Salesforce API Version
Log in into your Salesforce org and go to Setup
In the Quick Find field, type apex, then select Apex Classes from the results
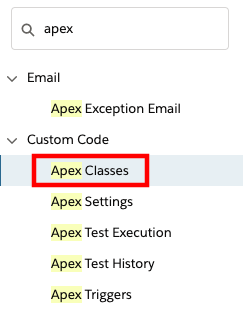
- Select New

- Select the Version Settings tab
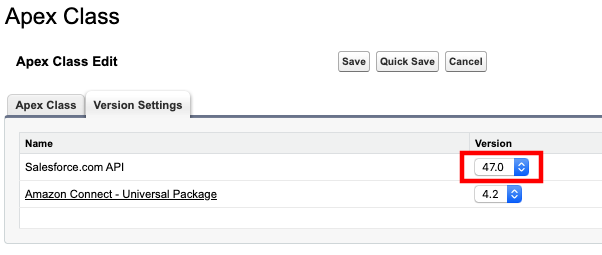
- Note the Salesforce.com API version in your notepad. The pattern of this value is
vXX.X.
Create a New Connected App
To leverage the full potential of the integration, Salesforce data needs to be accessed from AWS environment. The package comes with a set of pre-built AWS Lambda functions to lookup, update and create Salesforce objects within Amazon Connect Contact Flows. These Lambda function access Salesforce using the Salesforce REST API.
To get access to the environment, a Connected App must be configured with OAuth settings enabled.
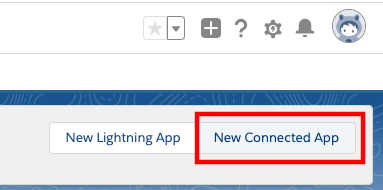
Log in into your Salesforce org and go to Setup
In the Quick Find field, type app manager, then select App Manager from the results
In the upper right corner, select New Connected App
- On the New Connected App form, enter a name for the Connected App, such as Amazon Connect Integration and press tab. This will populate the API Name automatically. Then provide a contact email address
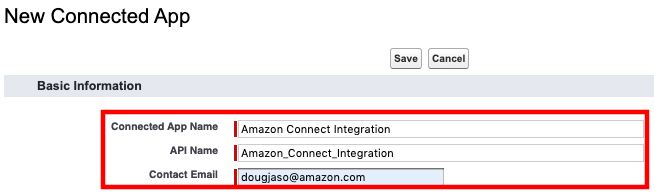
- Select the checkbox to Enable OAuth Settings
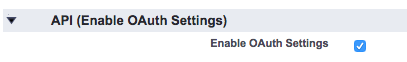
- Set the Callback URL to your domain url. Find the domain at Setup -> My Domain.
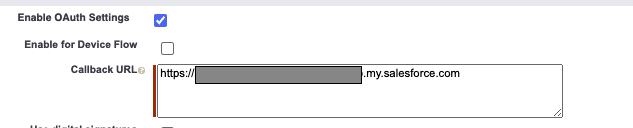
In the Selected OAuth Scopes section, select the following and add them to the Selected OAuth Scopes:
Access the identity URL service (id, profile, email, address, phone)
Manage user data via APIs (api)
Select the checkbox for Require Secret for Web Server Flow, and the checkbox for Require Secret For Refresh Token Flow
The API (Enable OAuth Settings) section should now look like this
Select Save at the bottom of the screen.
Select Continue on the New Connected App page
You should now be at the new app's page
Copy the value for Consumer Key to your notepad
Select Click to reveal next to Consumer Secret and copy the value to your notepad
At the top of the detail page, select Manage
On the Connected App Detail page, select the Edit Policies button
Set Permitted Users to Admin approved users are pre-authorized and choose OK on the pop-up dialog
Set IP Relaxation to Relax IP restrictions
The OAuth Policies section should now look like the following
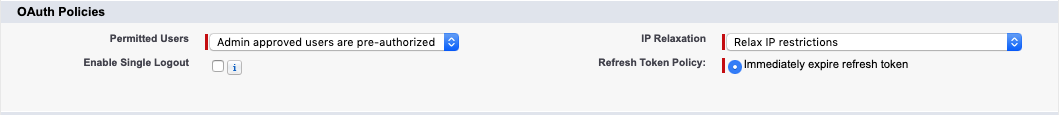
- Select Save
Create a new API user
The Lambda functions authenticate with Salesforce via user credentials. It is a common practice to create an API user account for this purpose.
Log in into your Salesforce org and go to Setup
In the Quick Find field, type profiles, then select Profiles from the results
Select New Profile
Provide a Profile Name, such as API_ONLY
From the Existing Profile dropdown, select System Administrator NOTE: You\'re advised to use a full Salesforce License for the user to be able to set the below permissions and have full access to avoid any other errors.
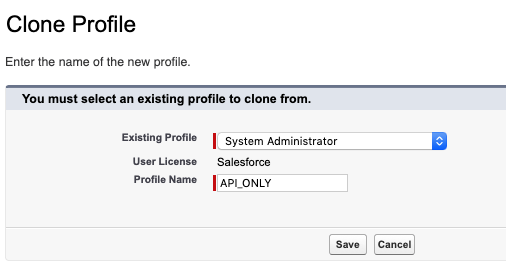
Select Save to create the new profile
Once the new profile page opens, scroll down to and select the System Permissions section
When the next page opens, select edit
Make sure the Lightning Experience User option is unselected

Select Save, and confirm the changes
Go back to the Profile Overview, scroll down, and select Password Policies
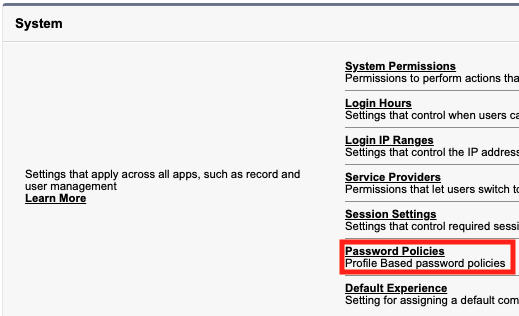
Select Edit.
Set User passwords expire in to Never expires NOTE: Failure to this may lead to production outages.
Select Save.
In the Quick Find field, type connect, then select Manage Connected Apps from the results
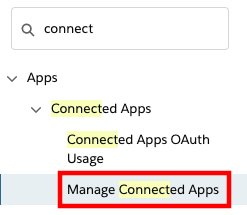
Select the app you have created earlier, Amazon Connect Integration
In the profiles section, select Manage Profiles
Select the new API_Only profile that you just created
Select Save at the bottom of the page
In the Quick Find field, type users then select Users from the results
Select New User
Set the required fields as:
a. Last Name: apiuser
b. Alias: apiuser
c. Email: provide a valid email address
d. Username: apiuser@<yoursalesforcedomain>.com
e. Nickname: apiuser
On the right-hand side, set User License to Salesforce
Set Profile to API_ONLY
Choose Save
In Quick Find, search for "Permission Sets". Select the AC_Administrator permission set.
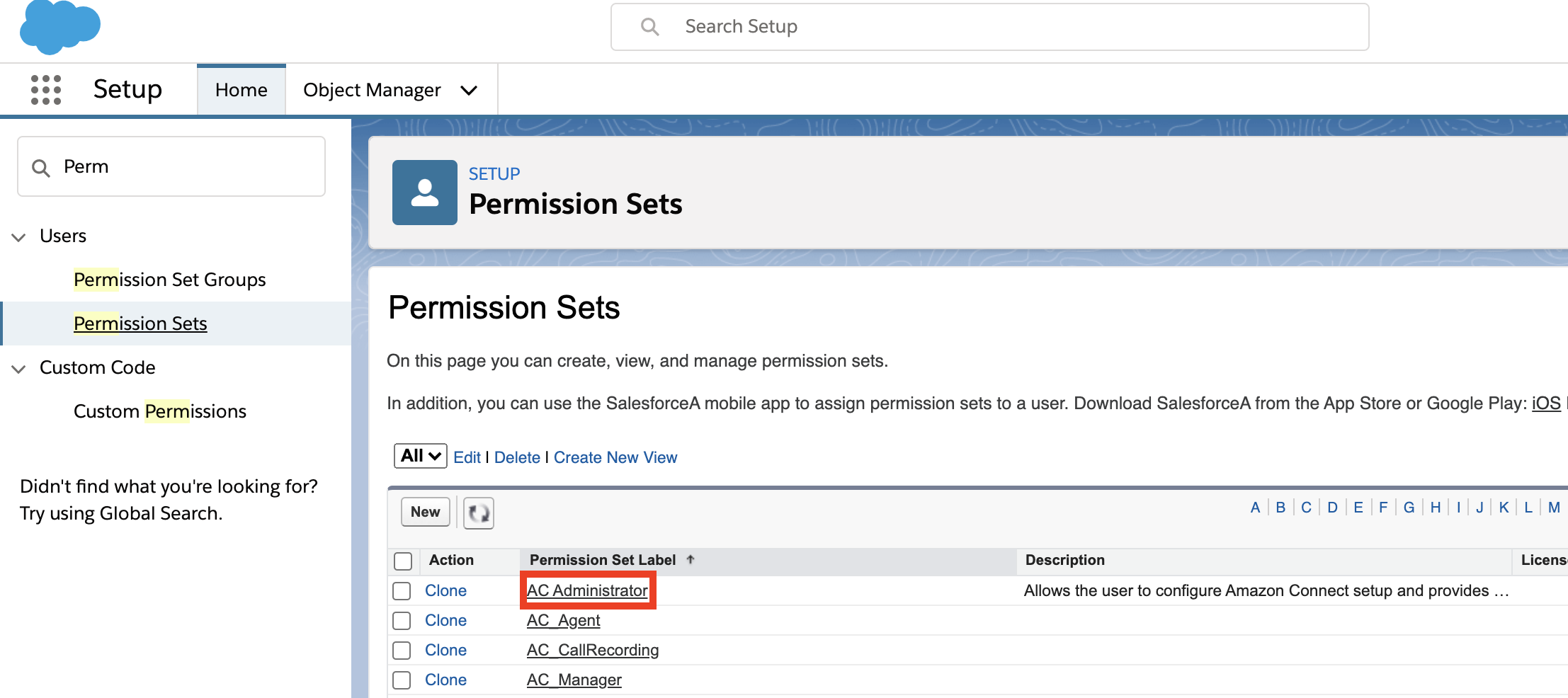
Select Manage Assignments. Add the apiuser you just created to the permission set.
A confirmation email with an activation link will be sent to the email address provided. Choose the link to activate your user and set their password
Fill out the form to set a password for the API user
Select Change Password. The API user will log into the Salesforce Classic view
Access the API user's personal settings by selecting the username in the top right corner, then choose My Settings
- In the Quick Find field, type security then select Reset My Security Token from the results
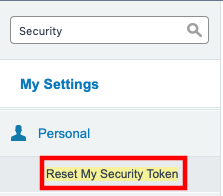
Select Reset Security Token. Your security token will be emailed to you
Copy the security token from the email to your notepad
Allowing the API user to authenticate using password
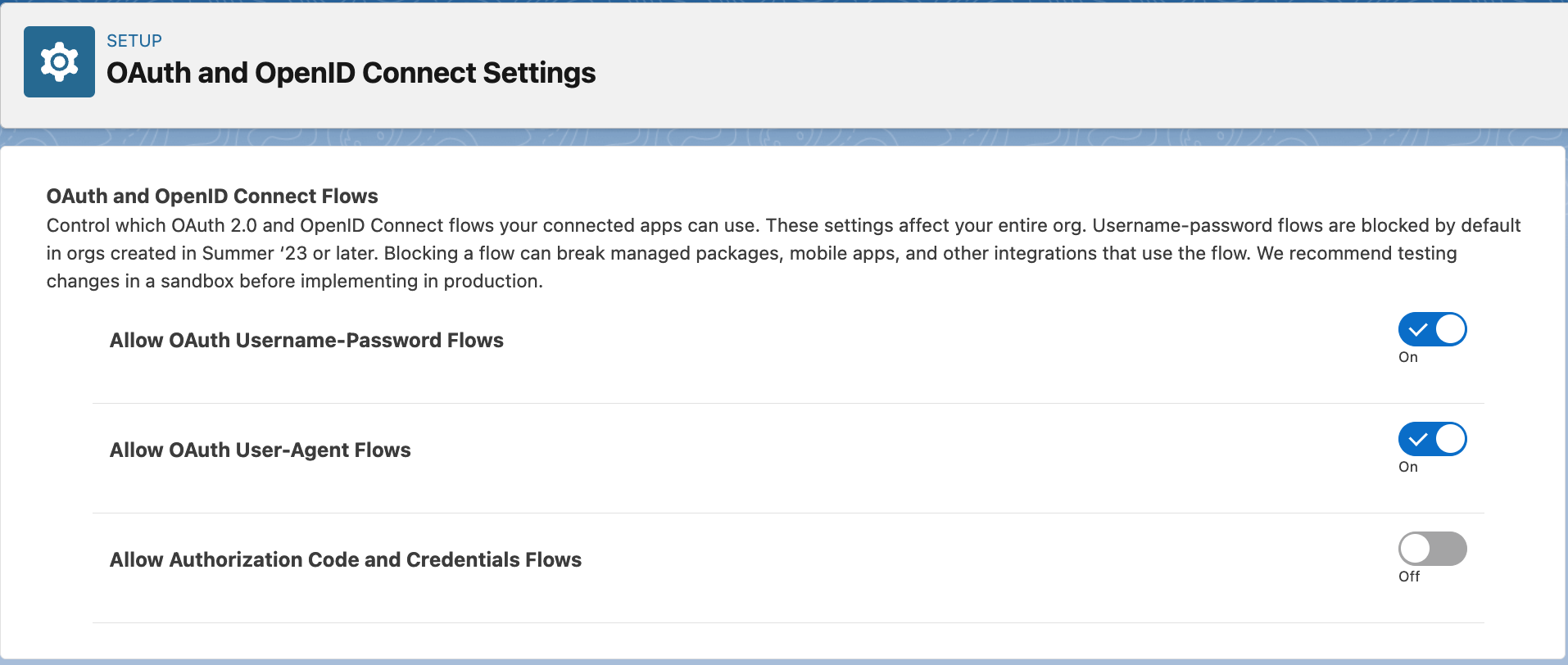
The api user created above authenticates using username-password flow in Salesforce. This flow needs to be unblocked and to do that, go to Setup and in the Quick Find box, search for OAuth and OpenID Connect Settings. After that, make sure that the toggles for Allow OAuth Username-Password Flows and Allow OAuth User-Agent Flows are turned ON, as shown in below image.
Gather Amazon Connect information
The last thing to do before you can install the Amazon Connect Salesforce Lambda Package is gather some details about your Amazon Connect instance. These will be used during the package installation.
In a new browser tab, login to the AWS console
Navigate to the Amazon Connect Console
Select your Instance Alias
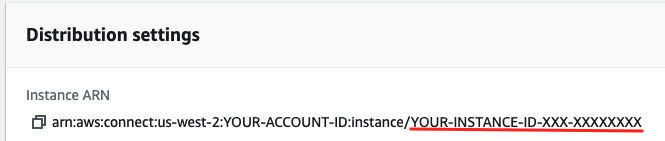
On the Overview page for your instance, copy the string following instance/ in the Instance ARN and paste it to your notepad. This is your Instance ID.
In the left nav, select Data storage
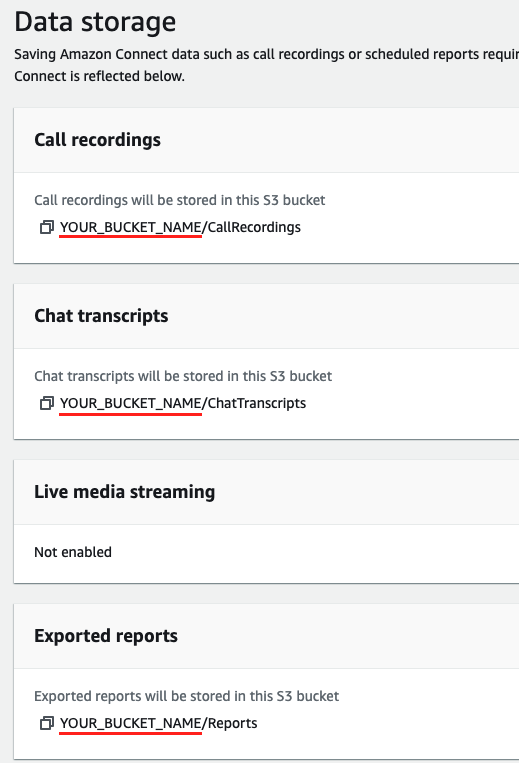
On the Data storage page, copy the S3 bucket names for your Call recordings and Exported Reports. The bucket name is everything preceding the first / in the XX will be stored here sections
In the left nav, select Data streaming
Note the name of the Kinesis stream configured in the Contact Trace Records section, then select Create a new Kinesis Stream. This will take you to the list of Kinesis streams configured in this region.
Select the Kinesis stream name that matches what was configured in the previous step
On the stream detail page, copy the entire value for Stream ARN

Store Salesforce Credentials in AWS Secrets Manager
To ensure that your Salesforce credentials are secure, the Lambdas require that the credentials are stored in AWS Secrets Manager. AWS Secrets Manager is a highly secure service that helps you store and retrieve secrets.
In a new browser tab, login to the AWS console
Make sure you are in the same region as your Amazon Connect instance. You can set the region by expanding the region selector in the upper right and choosing the region
Navigate to the Secrets Manager console
Select Secrets
Select Store a new secret
Select Other types of secrets
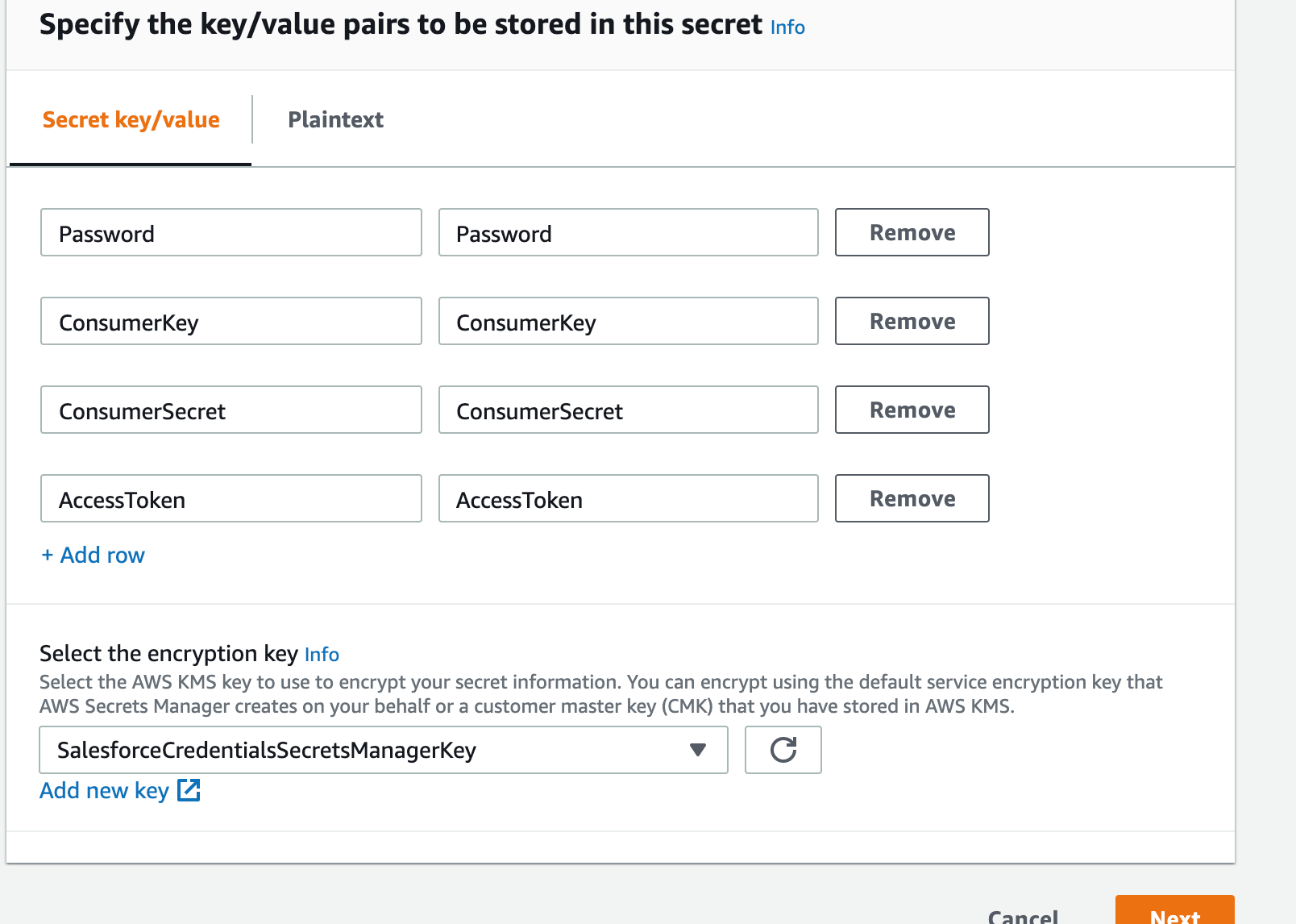
Make sure Secret key/value is selected
Enter key value pairs that match the following:
a. Key: Password, Value: the password for the API user that you configured in the previous section
b. Key: ConsumerKey, Value: the Consumer Key for the Connected App you created in the previous section
c. Key: ConsumerSecret, Value: the Consumer Secret for the Connected App you created in the previous section
d. Key: AccessToken, Value: this is the access token for the API user that you configured in the previous section
For the encryption key, click Add new key
Select Create Key
Make sure key type is set to symmetric
Give your key an alias, like SalesforceCredentialsSecretsManagerKey
Click Next
Select administrators you want to have access permission to change the key policy. Make sure you are being as restrictive as possible
Click Next
Select the users and roles you want to have access to the Salesforce credentials in Secrets Manager. Make sure you are being as restrictive as possible
Click Next
Click Finish
Click on the managed key that you just created (which is SalesforceCredentialsSecretsManagerKey in this case).
Note down the ARN. This is SalesforceCredentialsKMSKeyARN that will be used later when installing the Amazon Connect Salesforce Lambda package.
Navigate back to the Secrets Manager setup tab
Select the key you just created
Click Next
Give your secret a name, like SalesforceCredentials
Click Next
Make sure automatic rotation is disabled.
Click Next
Click Store
Select the secret you just created, and copy the Secret ARN
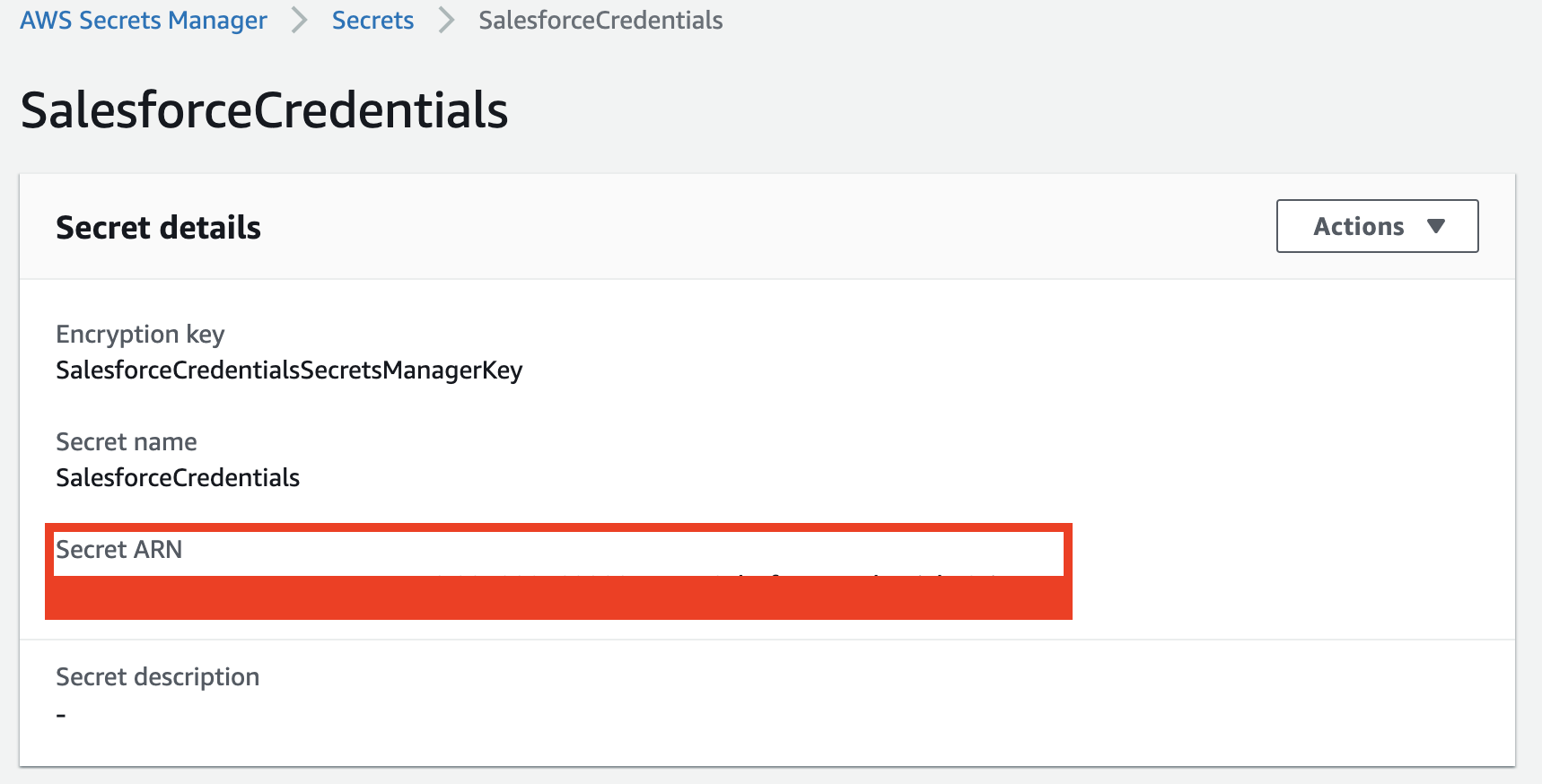
- You should now have all of the information you need to install the package
Install the Amazon Connect Salesforce Lambda package
Compatibility Table
The following table instructs users on the best CTI Adapter version to use with the corresponding lambda version. If a minor version for the CTI Adapter is not listed (ex. v5.21.1), it will be grouped with with its major version unless otherwise specified
| CTI Adapter Version | Lambda Version |
|---|---|
| v5.27 | v5.22 - v5.24 |
| v5.24 | v5.22 - v5.23 |
| v5.23.3 | v5.22 - v5.23 |
| v5.22 | v5.22 - v5.23 |
| v5.21 | v5.19 - v5.19.7 |
| v5.20 | v5.19 - v5.19.7 |
| v5.19 | v5.19 - v5.19.7 |
| v5.18 | v5.18 |
| v5.17 | v5.17 |
| v5.16 | v5.16 |
| v5.15 | v5.15 |
| v5.14 | v5.14 |
| v5.13 | v5.13 |
| v5.12 | v5.11 - v5.12 |
| v5.11 | v5.11 - v5.12 |
| v5.10 | v5.10 |
| v5.9 | v5.9 |
| v5.7 | v5.7 - v5.8 |
| v5.6 | v5.7 - v5.8 |
Instructions
In a new browser tab, login to the AWS console
Make sure you are in the same region as your Amazon Connect instance
Once you have selected the region, navigate to the Amazon Connect Console
Verify that the Amazon Connect instance that you wish to configure is listed
Once you have verified your Amazon Connect instance, Open the Serverless Application Repository Console
In the left navigation, select Available Applications

- In the search area, make sure that Public applications is selected, check the box for Show apps that create custom IAM roles or resource policies, and enter Salesforce in the search field, this will automatically filter the available packages
- Select AmazonConnectSalesForceLambda
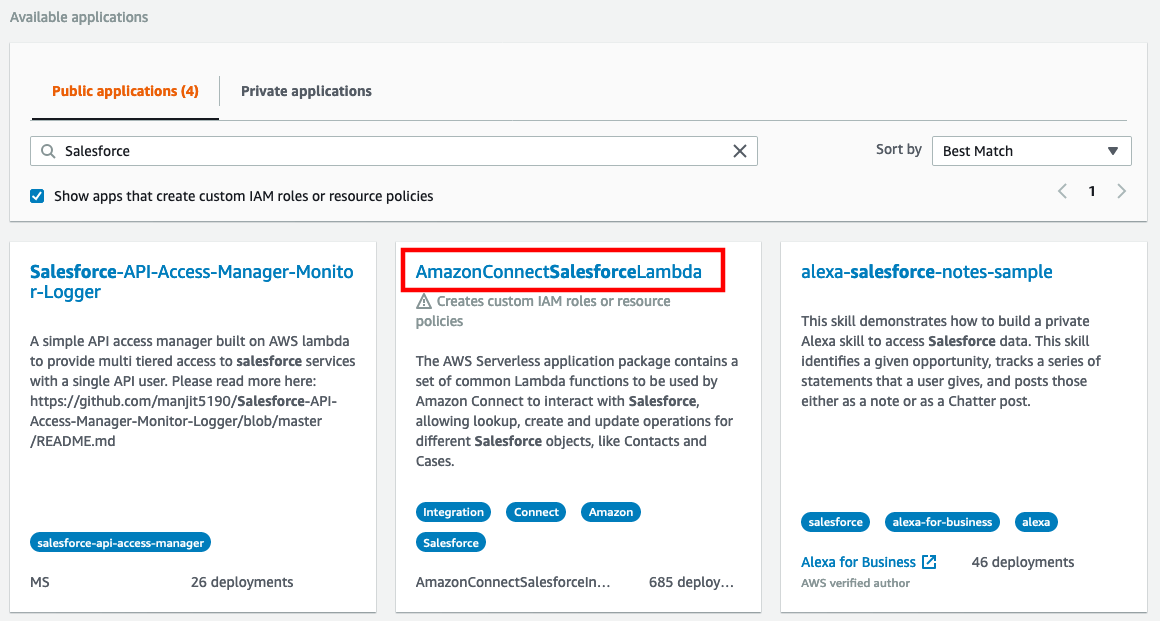
When the Application loads, scroll down to the Application settings section
Fill in the parameters using the data you gathered in your notepad in the previous section using the following notes:
Application name: You can accept the default here or change it as desired
AmazonConnectInstanceId: You Amazon Connect Instance Id. Only required if you enable real time reporting
CTRKinesisARN: This is the ARN for the Kinesis stream that was configured for Contact Trace Record streaming in Amazon Connect. This is the complete ARN. Amazon Kinesis Firehose is not supported.
ConnectReportingS3BucketName: This is the name of the S3 bucket used to store exported reports for your Amazon Connect instance. This is ONLY the bucket name, no sub-folders or suffixes
HistoricalReportingImportEnabled: true | false - if set to true, the package will include a feature to import Amazon Connect Queue and Agent Historical Metrics into your Salesforce Org. This feature requires you to provide ConnectReportingS3BucketName
LambdaLoggingLevel: DEBUG | INFO | WARNING | ERROR | CRITICAL - Logging level for Lambda functions
PrivateVpcEnabled: Set to true if functions should be deployed to a private VPC. Set VpcSecurityGroupList and VpcSubnetList if this is set to true.
RealtimeReportingImportEnabled: true | false - if set to true, the package will include a feature to publish Amazon Connect Queue Metrics into your Salesforce Org. This feature requires you to provide AmazonConnectInstanceId
SalesforceAdapterNamespace: This is the namespace for CTI Adapter managed package. The default value is amazonconnect. If a non-managed package is used, leave this field blank.
SalesforceCredentialsKMSKeyARN: This is the ARN for KMS customer managed key that you created in the previous section.
SalesforceCredentialsSecretsManagerARN: This is the ARN for the Secrets Manager Secret that you created in the previous section.
SalesforceHost: The full domain for your salesforce org. For example
https://mydevorg-dev-ed.my.salesforce.com. Please make sure that the host starts withhttps, and that the url ends with.my.salesforce.com. This url can be found inSetup->My Domain.SalesforceProduction: true | false - True for Production Environment, False for Sandbox
SalesforceUsername: The username for the API user that you configured in the previous section. Salesforce usernames are in the form of an email address.
SalesforceVersion: This is the Salesforce.com API version that you noted in the previous section. The pattern of this value is
vXX.X.TranscribeOutputS3BucketName: This is the S3 bucket where Amazon Transcribe stores the output. Typically, this is the same bucket that call recordings are stored in, so you can use the same value as found in ConnectRecordingS3BucketName. Not required if PostcallRecordingImportEnabled, PostcallTranscribeEnabled, ContactLensImportEnabled set to false.
VpcSecurityGroupList: The list of SecurityGroupIds for Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Not required if PrivateVpcEnabled is set to false.
VpcSubnetList: The list of Subnets for the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Not required if PrivateVpcEnabled is set to false.
AmazonConnectQueueMaxRecords: Enter record set size for list queue query. Max is 100.
AmazonConnectQueueMetricsMaxRecords: Enter record set size for queue metrics query. Max is 100.
CTREventSourceMappingMaximumRetryAttempts: Maximum retry attempts on failure for lambdas triggered by Kinesis Events.
ConnectRecordingS3BucketName: This is the name of the S3 bucket used to store recordings for your Amazon Connect instance. This is ONLY the bucket name, no sub-folders or suffixes
ContactLensImportEnabled: true | false - Set to false if importing Contact Lens into Salesforce should not be enabled.
PostcallCTRImportEnabled: true | false - Set to false if importing CTRs into Salesforce should not be enabled on the package level. This setting can be disabled on a call-by-call basis.
PostcallRecordingImportEnabled: true | false - Set to false if importing call recordings into Salesforce should not be enabled on the package level. This setting can be disabled on a call-by-call basis.
PostcallTranscribeEnabled: true | false - Set to false if post-call transcription should not be enabled on the package level. This setting can be disabled on a call-by-call basis.
TranscriptionJobCheckWaitTime: Time between transcription job checks
Once you have completed the form, select Deploy
Deployment will take some time, with status updates being provided by the UI. Once it has completely deployed, you will receive a notification on the screen
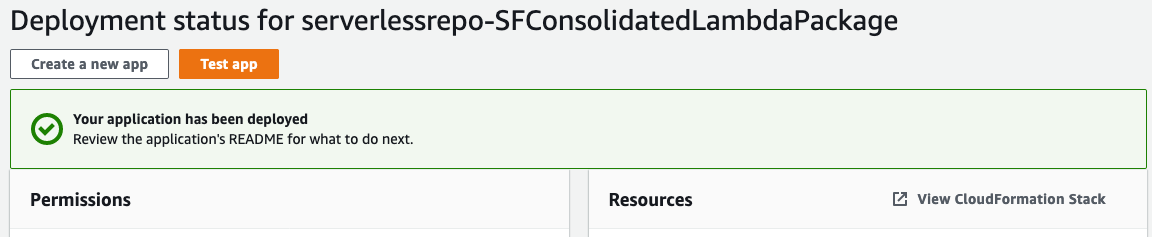
Test the Core Functionality
The package provides a core Lambda function (sfInvokeAPI) that supports multiple operations, like lookup, create and update. For the initial validation, sample events are provided within the function. Validating this function provides a good check that the installation and configuration is correct.
Validating the lambda functions requires the use of test events to simulate data coming into the function as it would in a typical deployment. Each function has a set of test event samples included to make validation easier.
Validate the core functionality
In a new browser tab, login to the AWS console
Open the AWS Lambda Console
In the Filter field, enter sfInvokeAPI and press enter, this will filter your list out to the core function that we just installed
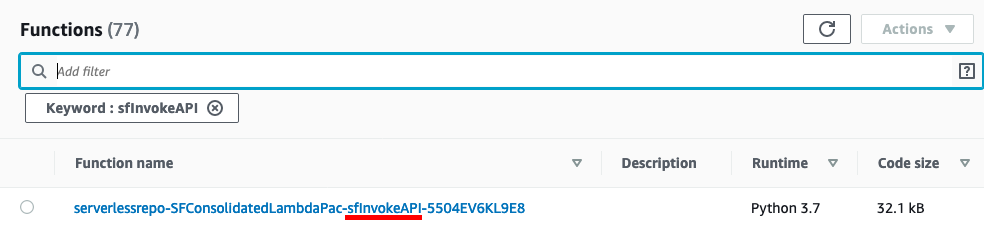
Select the function name. First, we will validate a phone number lookup.
In the Environment pane, double-click the event-phoneLookup.json file
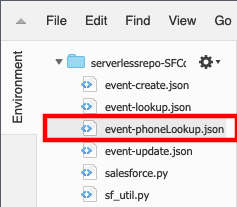
The test even JSON will open in the Lambda editor
Modify the value for sf_phone to match the phone number of the test contact you created when you setup the CTI adapter or for any valid contact in your Salesforce org\ NOTE: The phone number must be in E.164 format
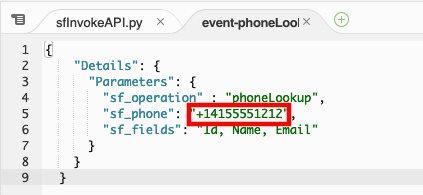
Select the entire JSON event and copy it, then close the event-phoneLookup.json tab.
In the top-right corner, select drop-down arrow next to Test and choose Configure test events
Select the radio button for Create new test event and provide an event name, for example: phoneLookup
Select the existing event JSON and delete it. Paste the modified JSON payload you copied from the event-phoneLookup.json file
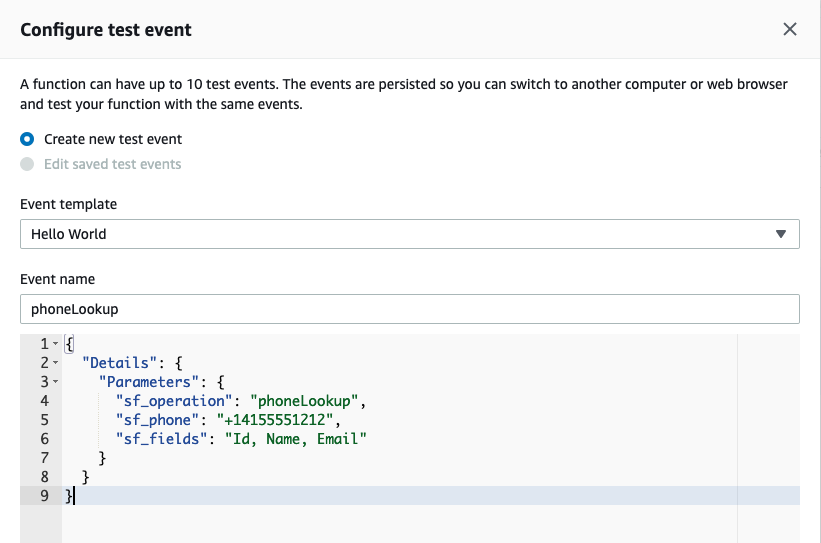
Select Create to save your test event
By default, your new test event should be selected in the drop-down list to the left of the Test button.
Select Test
If successful, the result will contain fields defined in "sf_fields" parameter in the invocation event
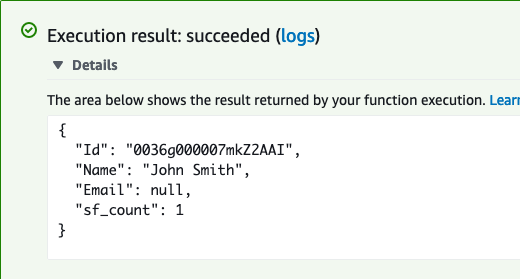
Copy the value for the Id key in the response. Next, we are going to use that Id to create a Case in Salesforce.
In the Environment pane, double-click the event-create.json file. Replace the existing ContactId value with the ID value you copied previously.
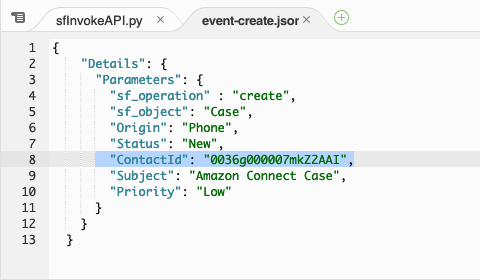
Select the entire JSON event and copy it, then close the event-create.json tab.
In the top-right corner, select drop-down arrow next to Test and choose Configure test events
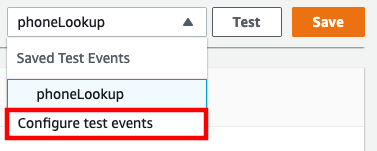
Select the radio button for Create new test event and provide an event name, for example: createCase
Select the existing event JSON and delete it. Paste the modified JSON payload you copied from the event-create.json file
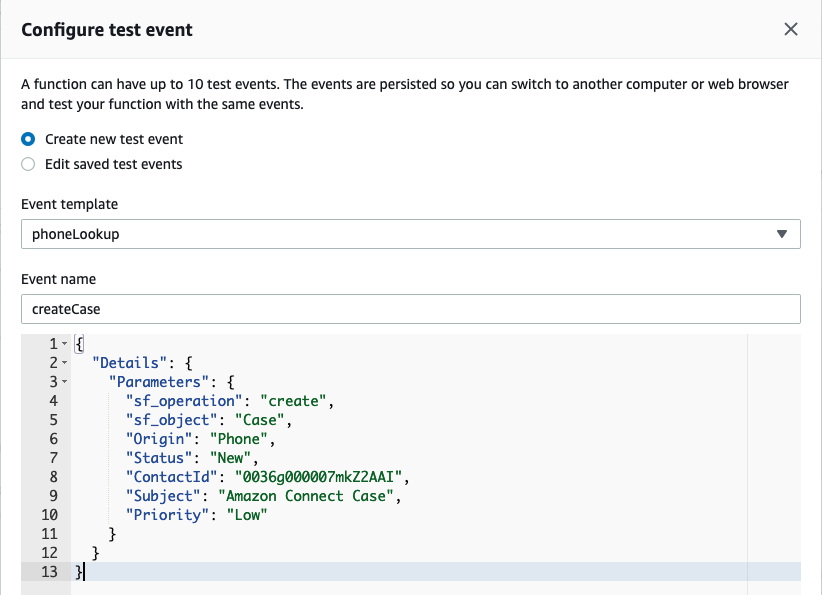
Select Create to save your test event
By default, your new test event should be selected in the drop-down list to the left of the Test button.

Select Test
If successful, the result will contain the Case Id
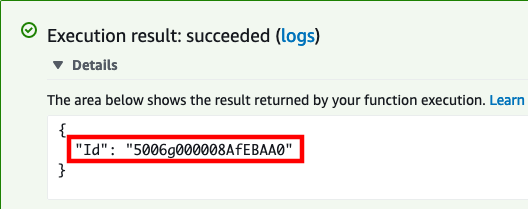
Copy the value for the Id key in the response.
When we created the case, the Status was set to New and the Priority to Low. We are going to use the update operation to close the case.
In the Environment pane, double-click the event-update.json file and replace the existing Case Id in "sf_id" parameter with the new one you copied from the last test result
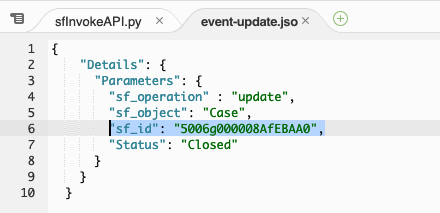
Select the entire JSON event and copy it, then close the event-update.json tab.
In the top-right corner, select drop-down arrow next to Test and choose **Configure test events
Select the radio button for Create new test event and provide an event name, for example: updateCase
Select the existing event JSON and delete it. Paste the modified JSON payload you copied from the event-update.json file
Select Create to save your test event
By default, your new test event should be selected in the drop-down list to the left of the Test button.
Select Test
If successful, the result will be the HTTP 204 No Content success status response code
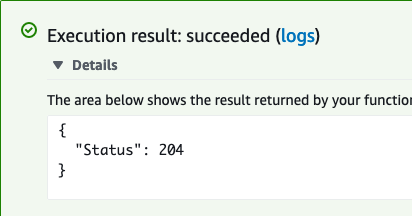
Log in into your Salesforce org and go to the Service Console
In the search box, change the object type to Cases and type Amazon Connect Case, then press enter

- You should find 1 case opened by the API user, and the status should be closed
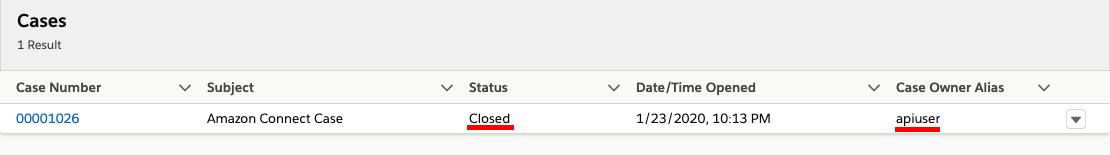
- You have completed core function validation
Allow Amazon Connect to Access the sfInvokeAPI Lambda Function
Once you have validated function, you can use the Amazon Connect console to add the sfInvokeAPI Lambda function to your Amazon Connect instance. This automatically adds resource permissions that allow Amazon Connect to invoke the function.
Add the Lambda function to your Amazon Connect instance
In a new browser tab, login to the AWS console
Navigate to the Amazon Connect Console
Select your Instance Alias
In the navigation pane, choose Contact flows.
- For AWS Lambda, select the function that includes sfInvokeAPI in the name
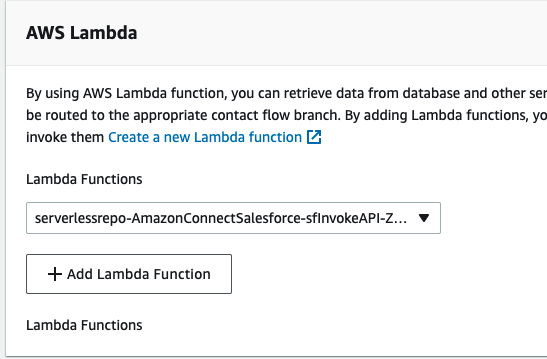
- Choose Add Lambda Function. Confirm that the ARN of the function is added under Lambda Functions.
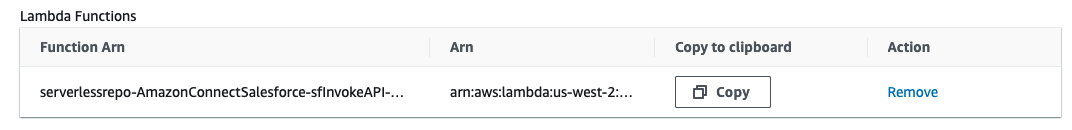
- The AWS Lambda function has been added to your Amazon Connect instance.